ECP Parallel
From HwB
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
== Contributions == | == Contributions == | ||
| − | |||
* [[User:Joakim|Joakim Ögren]] | * [[User:Joakim|Joakim Ögren]] | ||
* [mailto:[email protected] Marco Furter] | * [mailto:[email protected] Marco Furter] | ||
| Line 132: | Line 131: | ||
== Sources == | == Sources == | ||
| − | |||
* Microsoft MSDN Library: Extended Capabilities Port Specs | * Microsoft MSDN Library: Extended Capabilities Port Specs | ||
== Info == | == Info == | ||
| − | |||
* [http://www.microsoft.com/msdn Microsoft MSDN Library] | * [http://www.microsoft.com/msdn Microsoft MSDN Library] | ||
[[Category:Connector]] | [[Category:Connector]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Parallel]] | ||
Revision as of 10:43, 30 March 2007
ECP=Extended Capabilities Port
Contents |
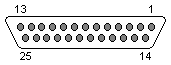
Pinout
25 PIN D-SUB FEMALE at the PC.
| Pin | Name | Dir | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nStrobe | |
Strobe |
| 2 | data0 | |
Address, Data or RLE Data Bit 0 |
| 3 | data1 | |
Address, Data or RLE Data Bit 1 |
| 4 | data2 | |
Address, Data or RLE Data Bit 2 |
| 5 | data3 | |
Address, Data or RLE Data Bit 3 |
| 6 | data4 | |
Address, Data or RLE Data Bit 4 |
| 7 | data5 | |
Address, Data or RLE Data Bit 5 |
| 8 | data6 | |
Address, Data or RLE Data Bit 6 |
| 9 | data7 | |
Address, Data or RLE Data Bit 7 |
| 10 | /nAck | |
Acknowledge |
| 11 | Busy | |
Busy |
| 12 | PError | |
Paper End |
| 13 | Select | |
Select |
| 14 | /nAutoFd | |
Autofeed |
| 15 | /nFault | |
Error |
| 16 | /nInit | |
Initialize |
| 17 | /nSelectIn | |
Select In |
| 18 | GND | |
Signal Ground |
| 19 | GND | |
Signal Ground |
| 20 | GND | |
Signal Ground |
| 21 | GND | |
Signal Ground |
| 22 | GND | |
Signal Ground |
| 23 | GND | |
Signal Ground |
| 24 | GND | |
Signal Ground |
| 25 | GND | |
Signal Ground |
Note: Direction is Computer relative Device.
Technical
This file is designed to give a basic overview of the port found in most newer PC computers called ECP Parallel port.
This file is not intended to be a thorough coverage of the standard. It is for informational purposes only, and is intended to give designers and hobbyists sufficient information to design their own ECP compatible devices.
Signal Descriptions:
nStrobe
This signal is registers data or address into the slave on the assering edge during .
data 0-7
Contains address, data or RLE data. Can be used in both directions.
nAck
Valid data driven by the peripheral when asserted. This signal handshakes with nAutoFd in reverse.
Busy
This signal deasserts to indicate that the peripheral can accept data. In forward direction this handshakes with nStrobe. In the reverse direction this signal indicates that the data is RLE compressed by being low.
PError
Used to acknowledge a change in the direction of transfer. High=Forward.
Select
Printer is online.
nAutoFd
Requests a byte of data from the peripheral when asserted, handshaking with nAck in the reverse direction. In the forward direction this signal indicates whether the data lines contain ECP address or data.
nFault
Generates an error interrupt when asserted.
nInit
Sets the transfer direction. High=Reverse, Low=Forward.
nSelectIn
Low in ECP mode.
Contributions
Sources
- Microsoft MSDN Library: Extended Capabilities Port Specs